Whether you have had a heat pump before or are considering making the switch, it’s important to know what you are getting before committing to such a big purchase. With every option, there are both pros and cons, so our hope is that more information can help you choose the right system for your priorities, budget, and comfort.
What is a heat pump?
Heat pump systems pump heat from one place to another by using a compressor and circulating a liquid or gas refrigerant. This process can also be reversed to provide air conditioning. There are four different kinds of heat pumps.
-
Ductless Heat Pumps:
A ductless heat pump requires less installation since it does not depend on ductwork within the home. These systems provide both heating and cooling. Key benefits include efficiency, low maintenance, and minimal energy costs. Ductless heat pumps work well alone or in conjunction with radiant floor heat.
-
Ducted Air Source Heat Pumps:
These heat pumps require installing or existing ductwork. However, they can reduce electricity costs by up to 50% compared to electric heating systems such as furnaces and baseboard heaters. Be advised that it’s essential to do your research when choosing this type of heat pump, as older models tend to not be compatible with low outdoor temperatures.
-
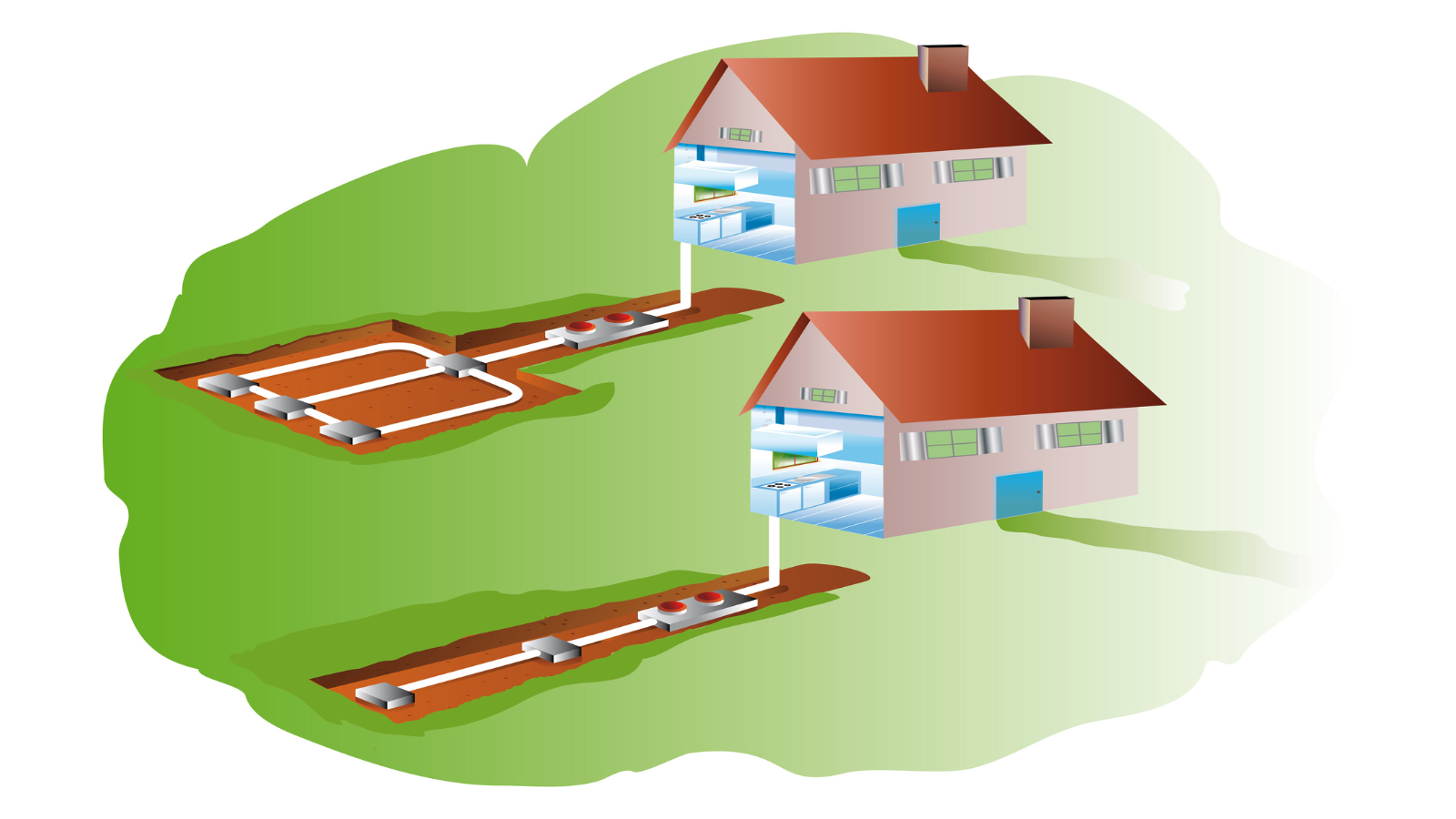
Geothermal Heat Pumps:
These systems use groundwater as a coolant. Groundwater is a renewable resource; therefore, this option appeals to those who would like a green alternative. Other benefits include reducing energy use by 30%-60%, controlling humidity, and lasting longer than traditional units. The cost of installation is high but the long-term savings are significant.
-
Absorption Heat Pumps:
This type of heat pump is newer to the market and is also known as a gas-fired heat pump. These units can use a wider variety of heat sources, making them very versatile.
Despite the many different varieties of heat pumps, here are the pros and cons overall:
PROS
- Heat pumps are considered safer than gas or oil furnaces since there is no danger from oil, natural gas or propane byproducts.
- These units are more efficient than their competitors and, therefore, will lower your energy bills
- Over time, you’ll notice that heat pumps require far less maintenance, repairs, and hidden costs (i.e., gas or oil refills)
- Due to high-efficiency, heat pumps reduce carbon emissions
- There is the added benefit of also providing air conditioning
- There are rebates currently available (up to $15,000 in Massachusetts)
CONS
- Some units can have a high upfront cost
- Specific units can be challenging to install
- Older units have trouble running in cold weather and can become less efficient in lower temperatures
- Sometimes, an additional heat source is optimal depending on the level of warmth desired
- Most have a shorter lifespan (10-15 years) compared to other types of heating systems (15-20 years)
If you know someone who can benefit from this blog, please share it.
If your question still needs answering or you’d like to schedule a consultation, contact the friendly team at Genove Oil & Air, and we’ll find a solution for your home or business.
Whether you need home heating oil or Bioheat delivery, or installation and service of oil & natural gas systems for HVAC, heating, and cooling—call us at 781-893-9191 or email us.